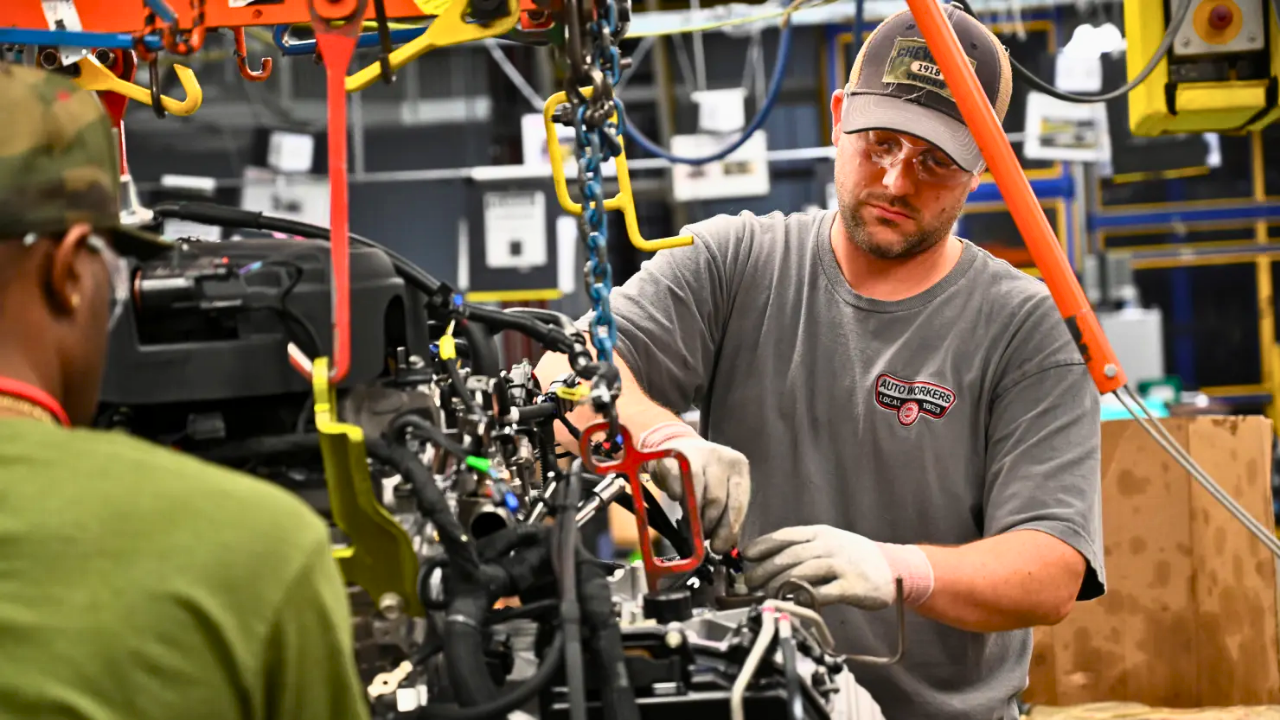

On October 29, 2025, General Motors (GM) made headlines with the announcement of approximately 1,750 job cuts across Michigan, Ohio, and Tennessee. Among these, 1,200 permanent layoffs at Detroit’s Factory Zero and 550 at Ultium Cells in Ohio represent a significant move for the auto giant. As the company takes a step back from its electric vehicle (EV) ambitions, this moment marks a critical crossroads for U.S. manufacturing, particularly in the growing EV sector.
The announcement reverberates far beyond GM, signaling challenges for the entire industry. The move is seen as a bellwether for the future of “green jobs” in America and raises crucial questions about the sustainability of the EV transition.
Why Did GM Slash Jobs?
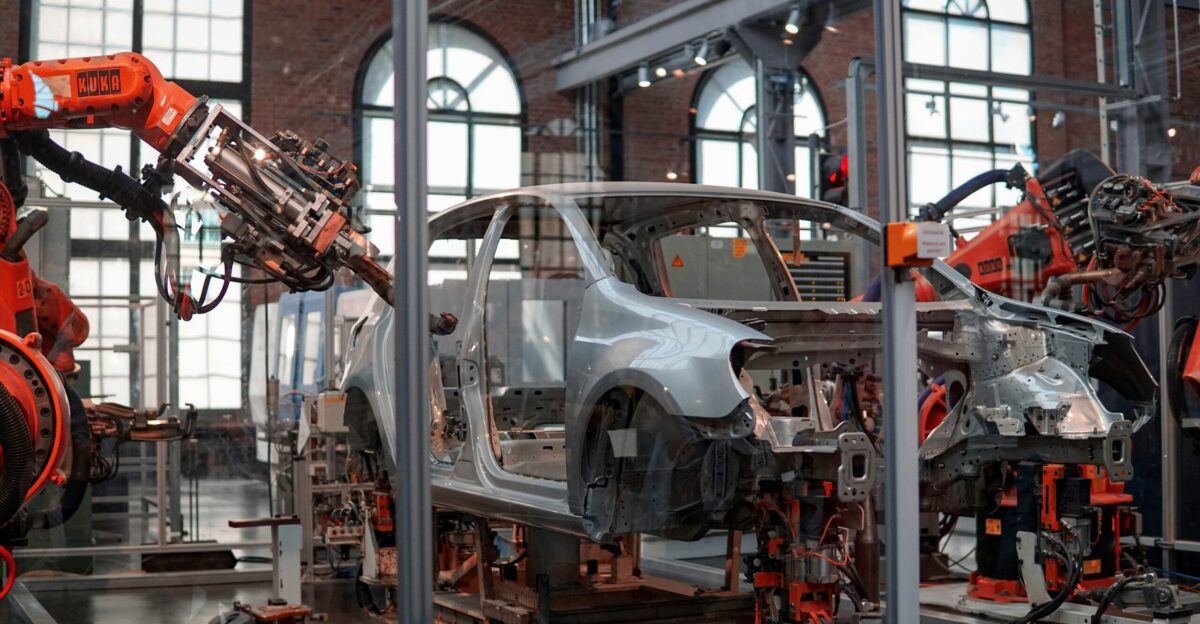

The layoffs are tied to slower-than-expected EV adoption and shifting regulatory landscapes. With the expiration of federal EV tax credits, GM cited the need for “structural changes to lower cost.” A significant pause in battery production at Ultium Cells plants in Ohio and Tennessee from January 2026 through mid-2026 added pressure.
This policy shift signals a pivotal moment in EV manufacturing, as the once-robust growth prospects now face stark reality. The expiration of federal incentives has placed additional strain on the market, pushing GM and other automakers to rethink their strategies.
Consumers Lose Access to EV Incentives

The expiration of the $7,500 federal EV tax credit on September 30, 2025, had a seismic impact on the electric vehicle market. Without the financial incentive, many consumers reconsidered their EV purchases, driving down demand.
With fewer incentives available, EVs became less affordable, intensifying the slowdown in the transition from gas-powered cars to electric vehicles. This change compounded GM’s troubles, contributing to the company’s decision to cut jobs.
Automakers Rethink Their EV Strategies

Following GM’s announcement, Ford and Stellantis revealed delays and cuts in their EV projects. They joined a growing list of automakers recalibrating their electric vehicle strategies. With demand uncertain and regulatory environments shifting, the industry is entering a phase of strategic retrenchment.
For manufacturers, the race to dominate the EV market may now be taking a more cautious, less ambitious tone. The recent shifts could indicate a broader rethink of EV production and future investments.
Battery and Parts Suppliers Feel the Pinch

The ripple effect from GM’s layoffs was swift. Dana Thermal Products, for example, shuttered its Auburn Hills, Michigan plant, laying off 200 workers. The plant’s closure, attributed to “lower-than-expected EV volumes,” reflects the broader trend of supply chain tightening.
As GM pulls back on its EV focus, parts suppliers and contractors face difficult decisions about their long-term viability in the sector. The contraction in battery and parts production may spread to other suppliers, contributing to regional economic strain.
International Trade and Supply Chains Disrupted

U.S. policy shifts and GM’s workforce cuts may have wider global repercussions. With reduced EV production, some analysts suggest the U.S. could become more reliant on foreign suppliers—especially for critical materials like lithium and cobalt.
This reliance on countries like China may reinforce its strong position in the EV market, with potential implications for global trade. The shift will likely affect international markets and the global balance of power in the EV sector.
Workers and Families Face Uncertainty

The approximately 1,750 GM workers facing layoffs across Michigan, Ohio, and Tennessee now find their futures uncertain. Many workers have lost steady incomes, and local economies in Michigan, Ohio, and Tennessee are grappling with the economic fallout.
For some, the layoffs are permanent; for others, they face the grim prospect of long-term temporary unemployment, with little clarity on when or if they will return to their roles. Families are now navigating financial strain, unsure of how long the disruption will last.
Policy Debates Intensify

GM’s job cuts have ignited a political firestorm. In Washington, lawmakers are debating the future of clean energy incentives. While some point to the expiration of EV tax credits as a key factor in the layoffs, others believe the market should dictate the pace of the transition.
This debate is now a key issue, influencing policy decisions about the green economy and its role in job creation. As lawmakers grapple with the issue, the direction of U.S. clean energy policy hangs in the balance.
Inflation and Investment Slowdown

GM’s move reflects broader economic trends, including slower regional growth. The layoffs and halted projects contribute to a cooling effect in the economy, with inflation concerns rising.
As companies adjust their strategies in response to the EV slowdown, investments in clean energy and related industries have stagnated, leaving investors with fewer opportunities to capitalize on what was once a burgeoning sector. The loss of momentum in clean energy threatens broader economic stability.
Retailers Adjust to Shifting Auto Demand

Auto retailers, facing reduced demand for electric vehicles, are adapting to changing market trends. Some industry observers note a renewed focus on traditional models as retailers respond to evolving consumer preferences.
The reduction in federal incentives for EVs has forced dealerships to adapt to a market that is recalibrating around affordability and practicality. Consumers are now more hesitant to embrace EVs, shifting their attention to vehicles they feel are more reliable in the short term.
Hospitality and Service Sectors Brace for Impact

The hospitality industry in auto-dependent regions may experience economic pressure following the layoffs. Local businesses—such as hotels, restaurants, and service providers—could be affected by overall reduced spending in these communities.
As workers tighten their belts, consumer spending in affected areas is expected to slow, amplifying the economic shock felt beyond factory gates. This ripple effect could hurt businesses that are already struggling to recover from previous disruptions.
Knock-On Effects for Related Industries

The broader impact of GM’s layoffs is being felt across industries connected to automotive manufacturing. Suppliers of auto parts, plastics, and logistics companies have seen their orders decrease, leading to layoffs and plant closures.
As GM scales back its EV production, the entire automotive supply chain faces uncertainty, exacerbating the impact on regional economies. This contraction will have lasting effects on industries that depend on the auto sector for business.
Global Consumers Face Shifting Choices

Consumers worldwide may soon feel the effects of GM’s EV pullback. As the U.S. reduces its electric vehicle output, foreign automakers—particularly Chinese companies—are well-positioned to fill the gap.
For global consumers, this means fewer choices and potentially higher prices as competition wanes and manufacturing shifts toward overseas markets. As the U.S. retracts its EV ambitions, international manufacturers are poised to capitalize on the void.
Health and Lifestyle Implications

Slower EV adoption may delay progress toward improved air quality and reducing carbon emissions. Reduced uptake of electric vehicles means gasoline-powered cars will remain prevalent, which continues to contribute to air pollution and climate change.
This setback delays the progress toward cleaner air and a healthier planet, with direct consequences for future generations. Reduced EV adoption weakens efforts to combat climate change and pollution.
Cultural and Environmental Debate Intensifies

The GM layoffs have reignited debates over the future of green jobs and economic stability. Advocates argue that strong, consistent policy support is essential for sustaining green job growth, while critics challenge the speed of electrification.
The debate pits economic security against environmental responsibility, forcing a reconsideration of how to balance the two priorities in policy. How the U.S. navigates this divide will shape its environmental future.
Who Gains, Who Suffers?

While American workers face the brunt of GM’s layoffs, foreign automakers—especially in China—are likely to benefit. With U.S. competition in EV production waning, these global competitors are poised to take advantage of the market shift.
At the same time, suppliers and local businesses in affected regions are among the unintended losers in this shakeup. As global competition intensifies, American manufacturers are struggling to maintain their edge.
Financial Markets React with Caution
GM’s $1.6 billion charge in Q3 2025 rattled investors and caused volatility in the automotive sector. With continued policy uncertainty and fluctuating demand, analysts predict that market instability could persist.
Investors are increasingly cautious about the future of the EV sector, which could impact stock portfolios and retirement funds tied to the industry. The volatility surrounding GM’s setbacks signals that the EV market’s path is far from certain.
What Should Consumers Do Now?

For consumers considering an EV purchase, the landscape has shifted dramatically. With the federal tax credit gone, state and local incentives may become the primary sources of support.
Experts advise consumers to weigh total ownership costs, considering both financial incentives and the broader market trends, as they explore their EV options moving forward. With the market in flux, consumers should stay informed about the latest developments.
What’s Next for U.S. Auto Manufacturing?

Looking ahead, U.S. automakers are expected to consolidate their resources and reassess their EV strategies. As GM and other manufacturers navigate the shifting policy environment, the future of U.S. auto manufacturing remains uncertain.
The industry’s survival depends on both market demand and government support to sustain the green revolution. The U.S. automotive sector’s next steps will shape its place in the global EV race.
Policy Ripples Shape the Future

GM’s layoffs are a stark reminder of how policy changes can dramatically affect industries and communities. The effects of the EV tax credit expiration extend far beyond one automaker, highlighting the interconnectedness of economic, political, and environmental decisions.
The event underscores the need for thoughtful, long-term policy planning to guide future transitions. How the government responds to these challenges will determine the future of green jobs and manufacturing in the U.S.