
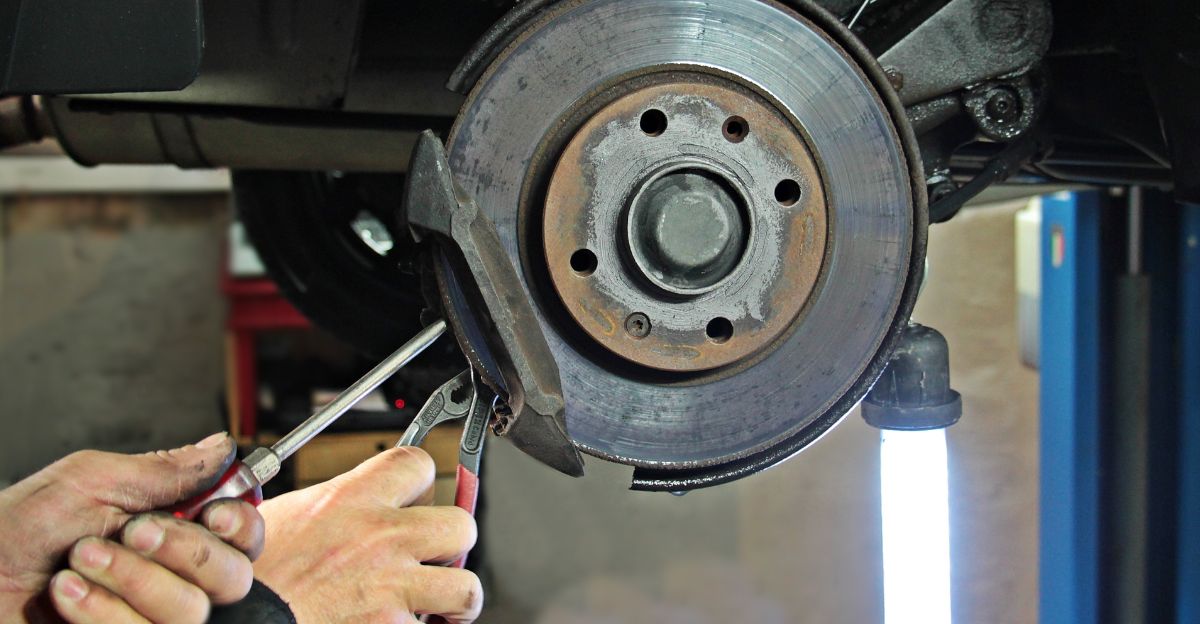
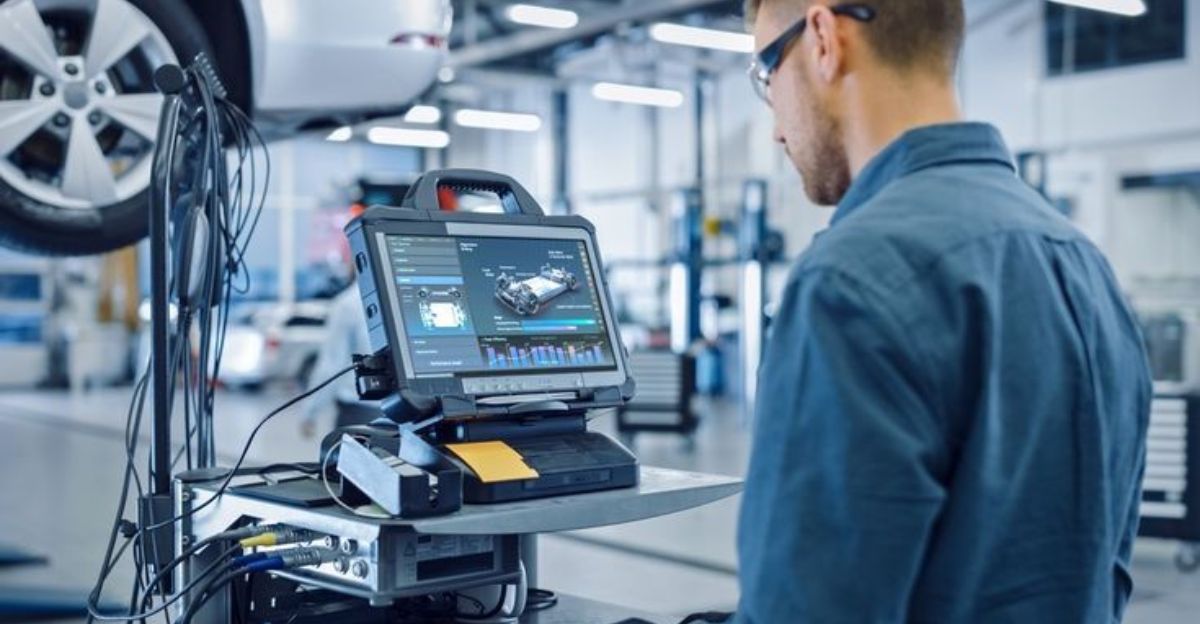
A man in Florida opens the trunk of his 2025 Hyundai Ioniq 5 N, tools in hand, ready to replace worn brake pads. He inserts the $2,000 J2534 adapter and launches the subscription software. A warning flashes: “DIYers are not permitted access.”
Frustrated, he logs in, pays the $60 weekly fee, and still—no brake service mode. Dealerships, by contrast, run the same procedure in seconds on a simple Android device.
Why Did Hyundai Restrict Brake Repairs?

Hyundai’s brake procedures require digitally disengaging the electronic parking brake before pads can be replaced. The company argues that interacting with these software-controlled components demands secure authentication and specialized tools.
But while dealerships use a simple Android-based tool that works instantly, owners face expensive hardware, weekly fees, and strict credential walls. This discrepancy has fueled speculation about whether the restrictions are truly safety-driven or part of a larger shift toward controlled repair ecosystems.
Immediate Impact: DIY Owners Shut Out

DIYers who purchased both the $2,000 adapter and the $60 subscription discovered the tool still wouldn’t allow brake servicing on 2025 Ioniq 5 N models. Several owners had their accounts terminated by the National Automotive Service Task Force, receiving the message: “DIYers are not permitted access.”
For enthusiasts who have maintained their own vehicles for decades, the sudden movement from wrenches to permissions marks a jarring—and costly—loss of autonomy.
Dealerships Gain an Advantage

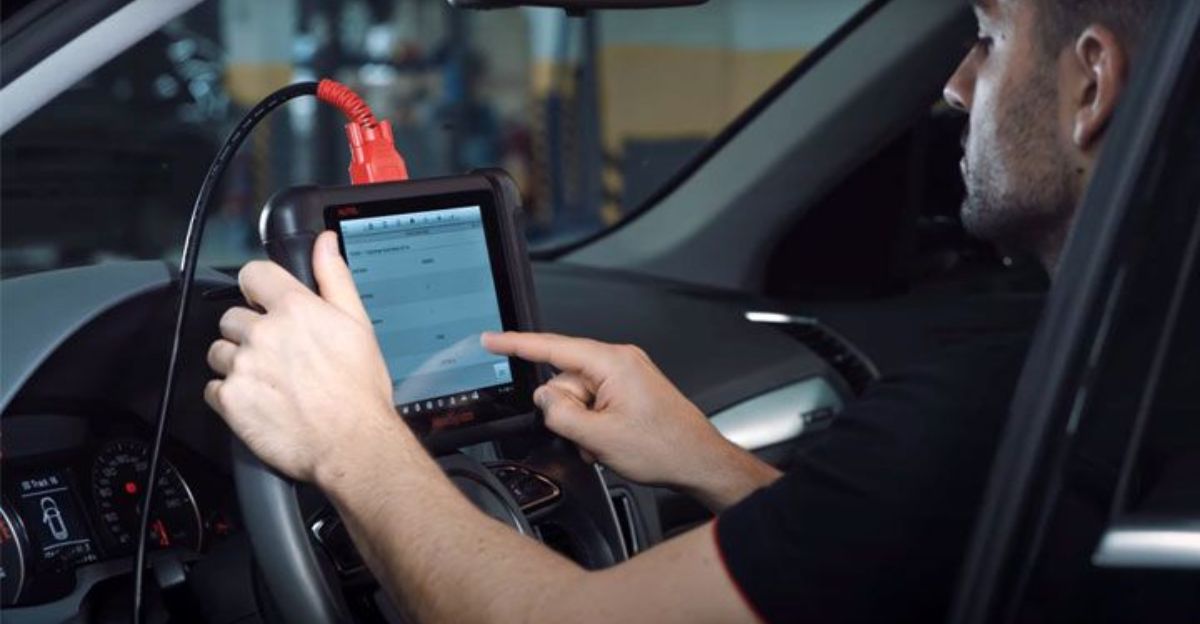
Hyundai dealerships enjoy full access using a proprietary Android-based diagnostic device that engages brake service mode instantly, bypassing the complex setup owners must purchase. This effectively creates an unprecedented two-tier system: dealerships get streamlined tools, while private owners face a $2,060 entry fee and still can’t complete repairs.
For many observers, the imbalance suggests a move that consolidates service revenue and nudges customers toward dealership dependency.
Aftermarket Tools and Independent Shops

Independent shops can, in theory, use supported J2534 devices—yet doing so requires not only the $2,000 hardware and ongoing subscriptions, but also professional credentials that individual mechanics or small shops may struggle to obtain.
This raises barriers for the aftermarket sector, potentially reducing competition and funneling repair work toward dealership networks. For smaller garages already operating on thin margins, the move could represent a meaningful threat to long-term viability.
International Implications: U.S. Focus, Global Questions

Although the lockout currently affects U.S. Ioniq 5 N owners, global right-to-repair advocates see this as a potential template for other markets.
Hyundai sold ~28,000 Ioniq 5 units in the U.S. in 2024, and if this approach expands internationally, millions of EV owners worldwide could see long-standing maintenance freedoms restricted. The case is now being watched as a potential blueprint for how software-controlled vehicles may redefine repair access globally.
Human Story: Frustration and Distrust

One Ioniq 5 N owner, after purchasing both the adapter and subscription, described discovering the system didn’t work as “infuriating,” adding, “My blood is boiling.”
With no official workaround and account access revoked despite payment, trust in Hyundai’s support for its enthusiast community has eroded. For many longtime DIYers, this moment represents more than a technical hurdle—it’s the feeling that their mechanical heritage is being digitally taken away.
Political Response: Calls for Regulation

Right-to-repair advocates immediately urged lawmakers to investigate Hyundai’s practices, framing them as an escalation in the broader fight previously centered on agricultural equipment.
They argue that placing routine safety-critical service behind expensive hardware and subscriptions undermines consumer rights and inflates maintenance costs. With EV adoption accelerating, legislators now face mounting pressure to determine whether automakers can legally gatekeep the tools required for basic vehicle upkeep.
Economic Ripple: Rising Maintenance Costs

At minimum, DIY access requires $2,060 for a single week. Maintaining year-round access would cost $3,120 annually—a stark contrast to the $50–80 typical cost of brake pads.
With dealerships commonly charging $150–300, the software lock effectively converts a low-cost DIY job into a mandatory $70–220 markup per service. Across an estimated 14,000 U.S. owners likely to attempt their own brake work, this represents millions in collective added costs.
Retailer Strategies: Shifting Service Models

Auto parts retailers and independent garages may reconsider their portfolios as software-locked repairs rise. Some may attempt to invest in the required diagnostic tools and seek authorization, while others pivot toward mechanical work on older vehicles. The shift challenges long-standing business models built on accessible parts and open repair procedures, signaling a future where service capacity depends less on skill and more on manufacturer-granted software permissions.
Hospitality and Fleet Operators Adjust

Rental fleets and commercial operators that normally perform in-house brake maintenance now face higher operating costs and logistical delays.
Without dealership-level access, fleets may be forced to outsource brake service entirely or negotiate specialized contracts. These added expenses—magnified across dozens or hundreds of vehicles—could translate into higher rental prices or reduced availability, reshaping cost structures in industries heavily dependent on predictable maintenance schedules.
Knock-On Effects: Toolmakers and Training

Diagnostic tool manufacturers and training providers may see increased demand as shops scramble to stay compliant with new authentication rules. Yet the requirement for professional credentials and paid subscriptions limits market reach, concentrating demand among larger operators rather than DIYers or small independents.
This creates a business environment where tool access becomes a gatekept commodity, reinforcing the emergence of an elite tier of manufacturer-approved repair networks.
Global Consumer Impact: A Warning Sign

For consumers worldwide, the Hyundai case is a stark warning: if one major automaker can restrict a basic maintenance task through software, others may follow. Right-to-repair organizations fear a domino effect across brands and markets.
The result could be a future where owners, despite paying full price for their vehicles, possess only conditional access to their repair functions—turning traditional ownership into something closer to a software-licensed relationship.
Health and Lifestyle: Delayed Repairs
When routine maintenance becomes locked behind costly equipment or inaccessible software, some owners may delay essential brake work. Over time, skipped repairs can compromise stopping performance, increase accident risk, and shorten component lifespan.
The broader concern is cultural: a world where vehicle safety depends not on skill or responsibility, but on subscription access. For many, this goes beyond inconvenience—it reshapes how safely and confidently people can operate their own cars.
Cultural Debate: Ownership vs. Access
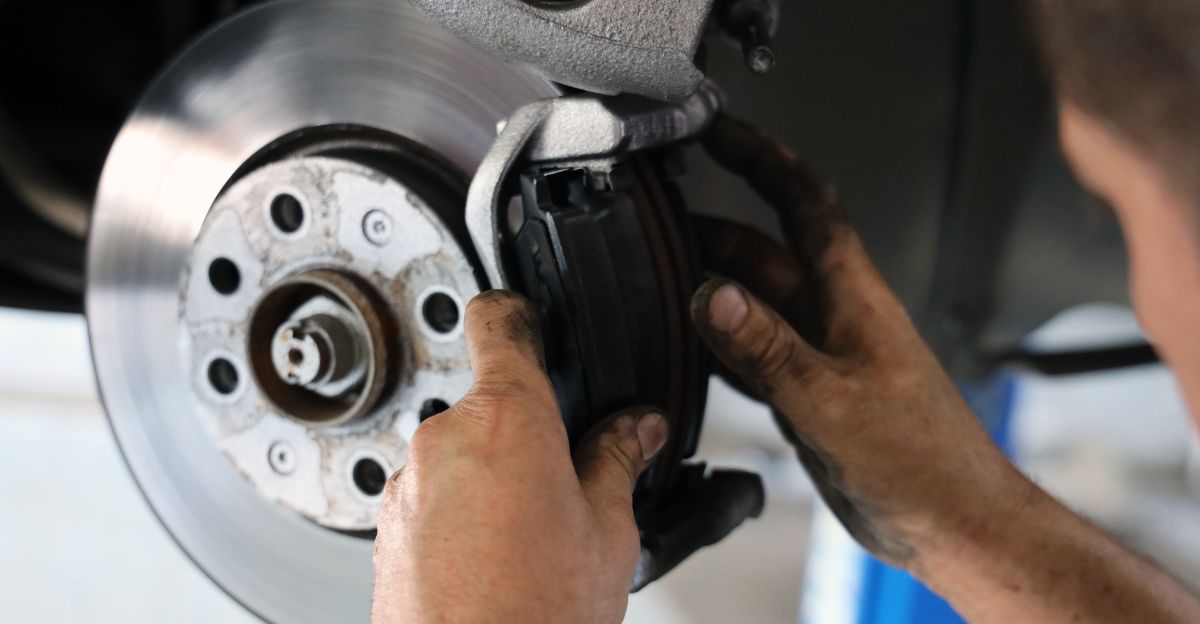

The conflict exposes a deeper cultural shift: the move from mechanical ownership to software-mediated access. For more than a century, brake pad replacement has symbolized self-reliance and control. Now, even a simple repair requires corporate authentication.
Critics argue this signals a belief-breaking revelation—EVs marketed as “low maintenance” can, in practice, become locked-down systems where the manufacturer holds the keys to repairs the owner once performed freely.
Winners and Losers: Dealerships Win, DIYers Lose
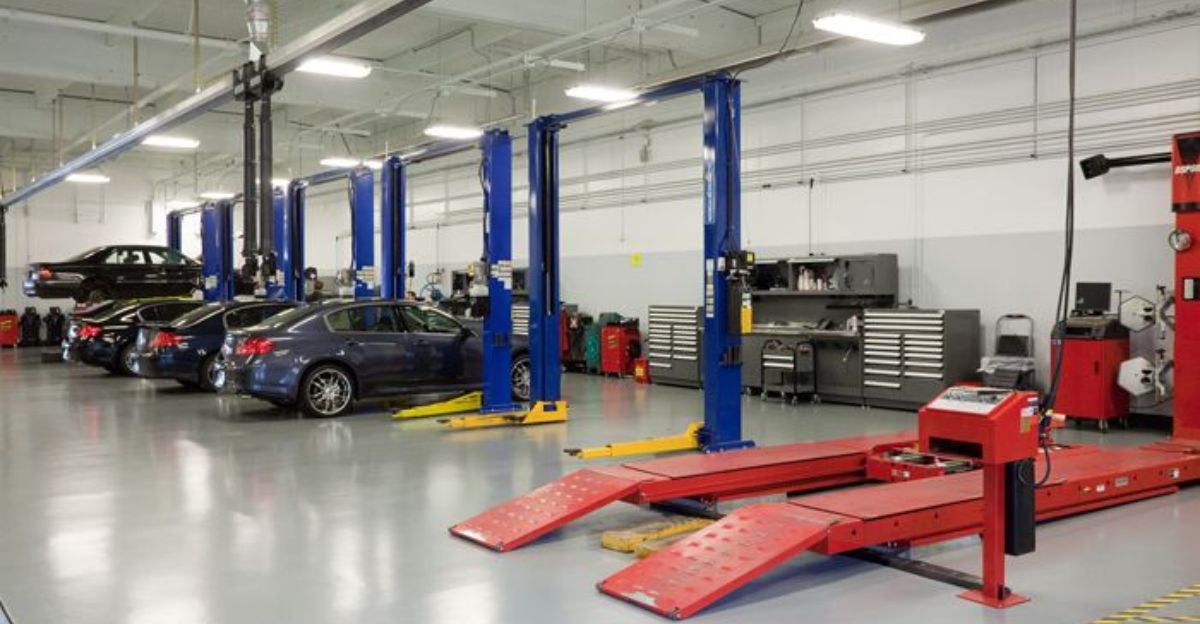

Dealerships emerge as clear beneficiaries, gaining increased service traffic and exclusive tool access. DIYers, independent mechanics, and cost-conscious consumers face steep barriers—financial, technical, and bureaucratic.
A job once costing under $100 in parts can now force a dealership visit, erasing generational knowledge and sidelining the skills of enthusiasts. For many, the lockout feels less like progress and more like a strategic narrowing of who gets to touch modern cars.
Market Speculation: Will Other Automakers Follow?

Industry analysts are watching closely. If Hyundai’s model proves profitable or defensible, other automakers may adopt similar restrictions. Investors see potential growth in dealership service volume and diagnostic tool licensing, while aftermarket suppliers brace for contraction.
A widespread shift could permanently reshape the economics of vehicle ownership, reducing consumer autonomy and solidifying automaker control over previously open maintenance ecosystems.
Consumer Advice: Navigating the New Landscape

Owners of the 2025 Ioniq 5 N should budget for dealership brake service unless regulatory or software changes occur. Those who prioritize DIY freedom may want to research models with fewer digital restrictions or advocate locally for right-to-repair legislation.
Before purchasing an EV, consumers should inquire about diagnostic access policies to avoid finding themselves locked into high subscription costs or inaccessible repair procedures.
What’s Next: Regulatory and Industry Shifts

Lawmakers are now under pressure to clarify repair rights in the age of software-defined vehicles. Regulations may eventually require automakers to provide functional, affordable access to essential repair tools.
Alternatively, the industry could continue drifting toward proprietary service ecosystems. Either direction will shape how future EVs are designed—determining whether ownership remains tangible or evolves into a licensed, subscription-bound experience.
The Big Picture: A Turning Point for Car Ownership

Hyundai’s brake lockout is more than an isolated controversy—it marks a turning point in the struggle between consumer autonomy and corporate control. As vehicles become increasingly digital, the boundaries of ownership grow blurry.
Whether this moment becomes a cautionary tale or the new normal depends on policy decisions, market reactions, and collective public pressure. What’s clear is that car ownership in the 2020s is being rewritten in software, one locked feature at a time.